Architecture
Components
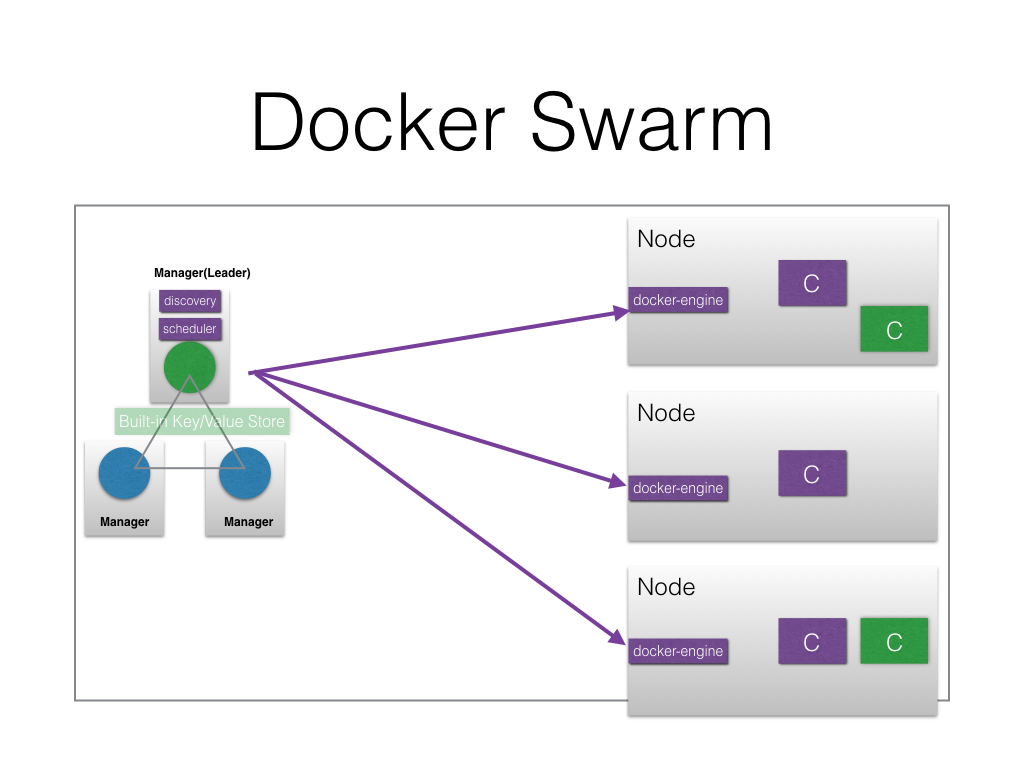
Manager
Scheduling
- Resource Availability
- Labels and constrains
- Engine label and constrains
- Node label and constrains
- Example
- Labels
- env=test, storage=ssh
- Constrains
- Nodes
- Strategy and affinity
- In Swarm mode only strategy supported is spread
Service Discovery
Runs an internal DNS server, which register are services created with Docker Swarm mode.
Nodes
Runs the contaniner using docker-engine.
As shown above, with Docker Swarm mode the order of creation is following:-
- Services
- tasks
- containers
- tasks
Defining an application
RSVP application
Docker Compose
version: '2'
services:
mongodb:
image: mongo:3.3
expose:
- "27017"
environment:
MONGODB_DATABASE: rsvpdata
networks:
- rsvpnet
web:
image: teamcloudyuga/rsvpapp
ports:
- "5000:5000"
environment:
MONGODB_HOST: mongodb
networks:
- rsvpnet
networks:
rsvpnet:
Docker Application Bundle
{
"Services": {
"mongodb": {
"Env": [
"MONGODB_DATABASE=rsvpdata"
],
"Image": "mongo@sha256:919d22a962b1913a2f57cbcd772689b4061cc05a7ccdf32a1900b58462c351d4",
"Networks": [
"rsvpnet"
],
"Ports": [
{
"Port": 27017,
"Protocol": "tcp"
}
]
},
"web": {
"Env": [
"MONGODB_HOST=mongodb"
],
"Image": "teamcloudyuga/rsvpapp@sha256:06923b50d69ee693ea4b3fc156f720d672a56508a3d66b0fe6f558715624e019",
"Networks": [
"rsvpnet"
],
"Ports": [
{
"Port": 5000,
"Protocol": "tcp"
}
]
}
},
"Version": "0.1"
}
High availablity of application
- Replicas of tasks running
- Multiple nodes
Service discovery and Load Balancing an application
- iptables
- classifies, modify and take decisions based on the packet
- IPVS
- load balancer at transport layer available in the Linux kernel
Autoscaling an application
- No inbuild primitive yet.
Rolling upgrade and rollback of an application
$ docker service update --image teamcloudyuga/rsvpapp:1 --update-delay 10s rsvp
Internally connecting to other application
- Each service get registred with the internal discovery service
- Applications can contact other using service VIP
Networking option to connect applications with-in the cluster
- Overlay network
- Network Plugins
Accessing the application from external world
- Once a service publishes a port, routing mesh maps the published port on all the nodes
- Any external client can query the published port on any nodes to reach the desired service
- A Load Balancer (HAProxy/Nginx) can be configured to map an endpoint to the pubished port on the nodes of the cluster.

Managing storage for application
- bind mounts
$ docker service create \ --name my-service \ --mount type=bind,source=/path/on/host,destination=/path/in/container \ nginx:alpine - named volumes
$ docker service create \ --name my-service \ --replicas 3 \ --mount type=volume,source=my-volume,destination=/path/in/container,volume-label="color=red",volume-label="shape=round" \ nginx:alpine
Detailed docs are available here.
Demo
Get the
$ git clone https://github.com/cloudyuga/container-orchestration.git
$ cd docker-swarm
$ export DO_TOKEN=adfvvfvs............
$ vagrant up --provider=digital_ocean
$ vagrant ssh manager
$ git clone https://github.com/cloudyuga/rsvpapp.git
$ cd rsvpapp
On Manager
root@manager:~/rsvpapp# docker swarm init --advertise-addr=<MANAGER_IP>
Swarm initialized: current node (<MANAGER_NODE_ID>) is now a manager.
To add a worker to this swarm, run the following command:
docker swarm join \
--token SWMTKN-1-<TOKEN> \
<MANAGER_IP>:2377
To add a manager to this swarm, run 'docker swarm join-token manager' and follow the instructions.
On Worker1
root@worker1:~# docker swarm join \
> --token SWMTKN-1-<TOKEN> \
> <MANAGER_IP>:2377
This node joined a swarm as a worker.
On Worker2
root@worker2:~# docker swarm join \
> --token SWMTKN-1-<TOKEN> \
> <MANAGER_IP>:2377
This node joined a swarm as a worker.
On Manager
$ docker info
$ docker service create alpine ping 8.8.8.8
$ docker service ps <serviceID>
$ docker sevice inspect <serviceID>
$ docker service update <serviceID> --replicas 4
$ docker service create --name web --publish 80:80 --replicas 4 nginx
Deploy the RSVP service manually
$ docker network create --driver overlay rsvpnet
$ docker service create --name mongodb -e MONGODB_DATABASE=rsvpdata --network rsvpnet mongo:3.3
$ docker service create --name rsvp -e MONGODB_HOST=mongodb --publish 5000 --network rsvpnet teamcloudyuga/rsvpapp
$ docker service ls
$ docker service inspect rsvp
$ docker service scale rsvp=5
$ docker service rm rsvp
$ docker service rm mongodb
Deploy the RSVP service with Docker Application Bundle
$ docker deploy rsvpapp
$ docker service ls
$ docker service inspect rsvpapp_web
$ docker service scale rsvpapp_web=4
Other Examples
$ docker service update --image teamcloudyuga/rsvpapp:v1 --update-delay 10s rsvp
$ docker service create --name util --network rsvp --mode global alpine sleep 200
$ docker service update stateful --constraint-add node.hostname==$HOSTNAME
$ docker service update stateful --limit-memory 100M
$ docker service update statful --mount-add type=volume,source=somename,target=/data
Managing Nodes
$ docker node update <node_name> --availability <active/pause/drain>
$ docker swarm promote
$ docker swarm demote
$ docker swarm leave
Destroy the setup
$ vagrant destory -f