Architecture
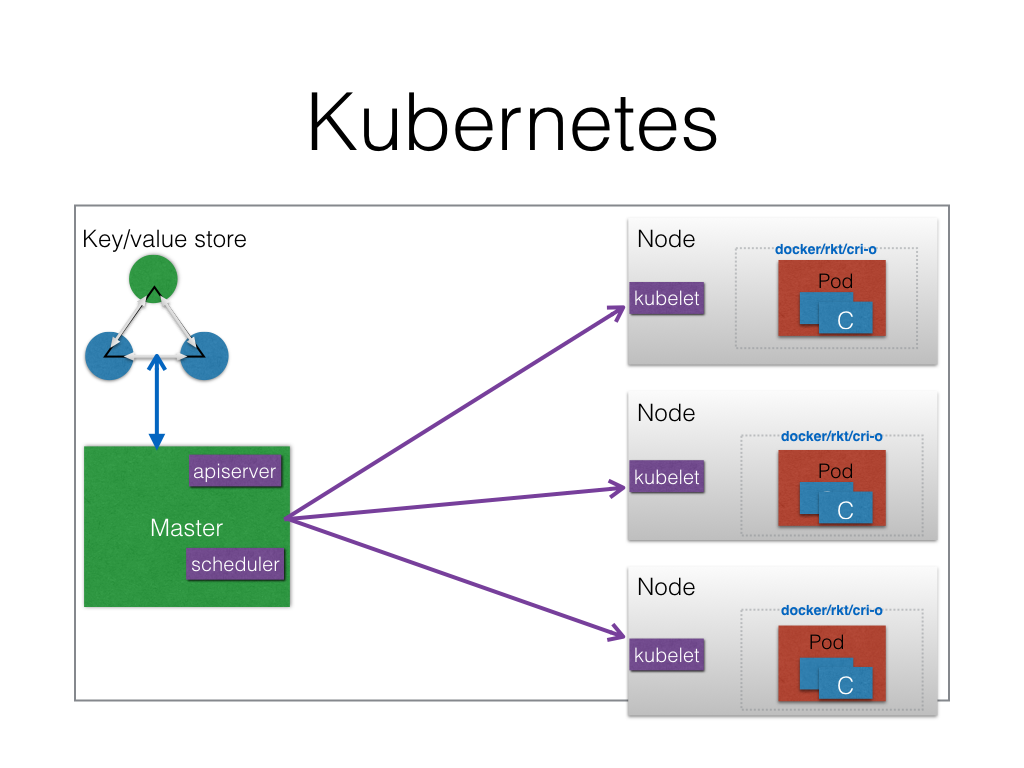
Components
Master
Apiserver
Schedulder
Nodes
Kubelet
kube-proxy
Container Engine
Key/Value Store
Key Concepts
- Containers
- Pod
- Label
- Selector
- Replication Controllers
- Replica Sets
- Deployment
- Services
- Volumes
Advance Resources
- Namespaces
- ConfigMaps
- Secrets
- Batch Jobs
- PetSets
- DaemoncSet
- Ingress
Defining an application
RSVP Application
Deployments
MongoDB
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: rsvp-db
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
appdb: rsvpdb
spec:
containers:
- name: rsvpd-db
image: mongo:3.3
env:
- name: MONGODB_DATABASE
value: rsvpdata
ports:
- containerPort: 27017
RSVP App
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: rsvp
spec:
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: rsvp
spec:
containers:
- name: rsvp-app
image: teamcloudyuga/rsvpapp
env:
- name: MONGODB_HOST
value: mongodb
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
Services
MongoDB
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mongodb
labels:
app: rsvpdb
spec:
ports:
- port: 27017
protocol: TCP
selector:
appdb: rsvpdb
RSVP App
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rsvp
labels:
app: rsvp
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5000
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: rsvp
High availablity of application
- Pods Replicas
- Multiple nodes
- Multiple master
Service discovery of applications
- Services get registred with a DNS, which each node can access.
- With default installation, kube-dns service get delpoyed which
- registers new service's VIP
- resolves name to VIP
Load Balancing an application
- Internal
- kube-proxy
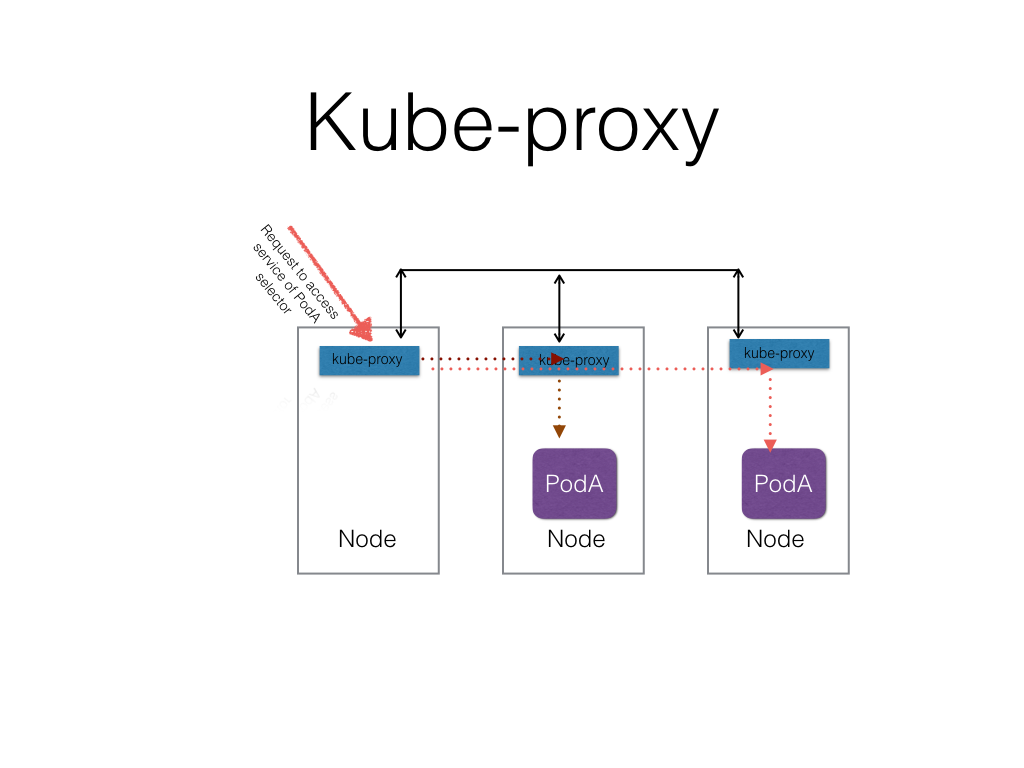
- kube-proxy
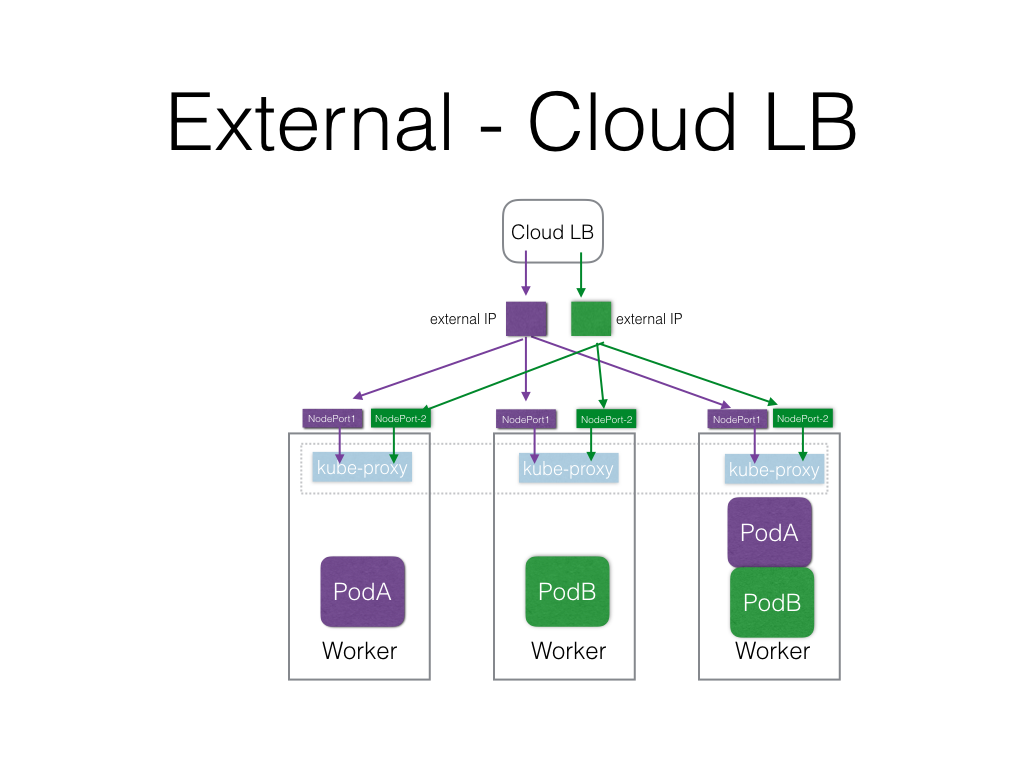
- External
Autoscaling an application
- Horizontal Pod Scaling
- Based on CPU usage now which uses heapster to collect CPU utilization.
- Custom matrics support is coming
Rolling upgrade and rollback of an application
- Using Deployments
Internally connecting to other application
- using serivce VIP
Networking option to connect applications with-in the cluster
- Flat Networking
- All containers talks to other containers without NAT
Accessing the application from external world
- LoadBalancer (requires Cloud Provider's support)
- NodePort
- External IP
- Igress
Managing storage for application
- Volumes are per pod. Even if container in a pod goes down, volume exists.
- To use a volume, a pod specifies what volumes to provide for the pod (the
spec.volumesfield) and where to mount those into containers(thespec.containers.volumeMountsfield).
Supported Volumes
emptyDirhostPathgcePersistentDiskawsElasticBlockStorenfsiscsiflockerglusterfsrbdcephfsgitReposecretpersistentVolumeClaimdownwardAPIazureFileVolumevsphereVolume
Demo
Download kubectl
$ curl -O https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.3.5/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
$ chmod +x kubectl
$ mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Configure kubectl
- Copy the share config file inside ~/.kube
$ mkdie ~/.kube $ cp <PATH>/config ~/.kube
Create the namespace
$ kubectl create namespace <username>
Get the current context
$ export CONTEXT=`kubectl config view | awk '/current-context/ {print $2}'`
Update the default namespace for the current context
$ kubectl config set-context $CONTEXT --namespace=<username>
Create a deployment
$ kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx --replicas=2 --port=80
List the pods and deployments
$ kubectl get pods
$ kubectl get deployments
Create a service and expose it using NodePort
$ kubectl expose deployment my-nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort
List the service
$ kubectl get services
Acccess the sevice using NodePort
Delete service and deloyment
$ kubectl delete svc my-nginx
$ kubectl delete deployment my-nginx
Deploying RSVP app
Clone the repo
$ git clone https://github.com/cloudyuga/container-orchestration.git
$ cd container-orchestration/k8s
Create db
$ kubectl create -f rsvp-db.yaml
$ kubectl create -f rsvp-db-service.yaml
Create web frontend
$ kubectl create -f rsvp-web.yaml
$ kubectl create -f rsvp-web-service.yaml
List
$ kubectl get deployments
$ kubectl get svc
Scale
$ kubectl scale --replicas=4 deployments/rsvp
Delete
$ kubectl delete deployments/rsvp deployments/rsvp-db
$ kubectl delete svc/mongodb svc/rsvp